+86-13349293098
+86-13349293098
Leave Your Message
-
 Contact Phone
Contact Phone -
 Contact WhatsApp
Contact WhatsApp -
 Contact Email
Contact Email



In the realm of modern machinery, the Slewing Circle Bearing stands out as an essential component, enabling the smooth rotational movement required for various applications. As defined by engineering expert Dr. John Smith, "The Slewing Circle Bearing is crucial for any equipment that requires a high degree of precision and heavy load-bearing capacity." This intricate mechanism is often found in cranes, excavators, and wind turbines, where its ability to support axial and radial loads simultaneously is vital.
The significance of the Slewing Circle Bearing extends beyond mere functionality; it symbolizes the intersection of engineering innovation and operational efficiency. As industries increasingly embrace automation and advanced machinery, understanding the role of Slewing Circle Bearings becomes paramount. Their applications not only enhance performance but also contribute to the longevity and reliability of equipment in demanding settings. This introduction sets the stage for a deeper exploration of the design, functionality, and diverse applications of Slewing Circle Bearings across various sectors.

Slewing circle bearings are crucial components in various types of machinery, providing the necessary support and rotation. These bearings consist of an outer ring, an inner ring, and rolling elements, typically balls or rollers, that facilitate smooth movement. The design is robust and adaptable, allowing for the transmission of axial, radial, and moment loads. The structure often includes gear teeth on the inner or outer ring, enabling controlled rotation when connected to drive systems.
When selecting a slewing circle bearing, it's essential to consider factors such as load capacity and environmental conditions. Proper lubrication is also key to maintaining performance and extending the bearing's life.
Tips: Regular maintenance and monitoring of the bearing's condition can prevent unexpected failures. Using appropriate seals can keep contaminants out, ensuring a longer lifespan and reliability in harsh conditions. Always consult technical specifications to ensure optimal compatibility with your machinery.
Slewing circle bearings are essential components in various types of machinery, providing crucial support for rotating elements. These bearings come in several types, each characterized by specific features tailored to meet different operational demands. One of the most common types is the ball slewing bearing, recognized for its simplicity and efficiency. It consists of a series of balls positioned between the inner and outer rings, allowing for smooth movement under axial and radial loads. This makes it particularly suitable for applications such as cranes, excavators, and other construction equipment.
In contrast, the roller slewing bearing utilizes cylindrical rollers instead of balls, offering higher load capacity and improved stability under heavy loads. This type of bearing is ideal for applications that experience considerable weight and stress, such as wind turbines and large industrial machinery. Additionally, the crossed roller bearing is designed with alternating layers of rollers, providing enhanced rigidity and precision in positioning. This is particularly beneficial in applications such as robotics and aerospace, where accuracy is paramount. Each type of slewing circle bearing serves a distinct role in ensuring the efficient operation of machinery, catering to different load requirements and movement dynamics.
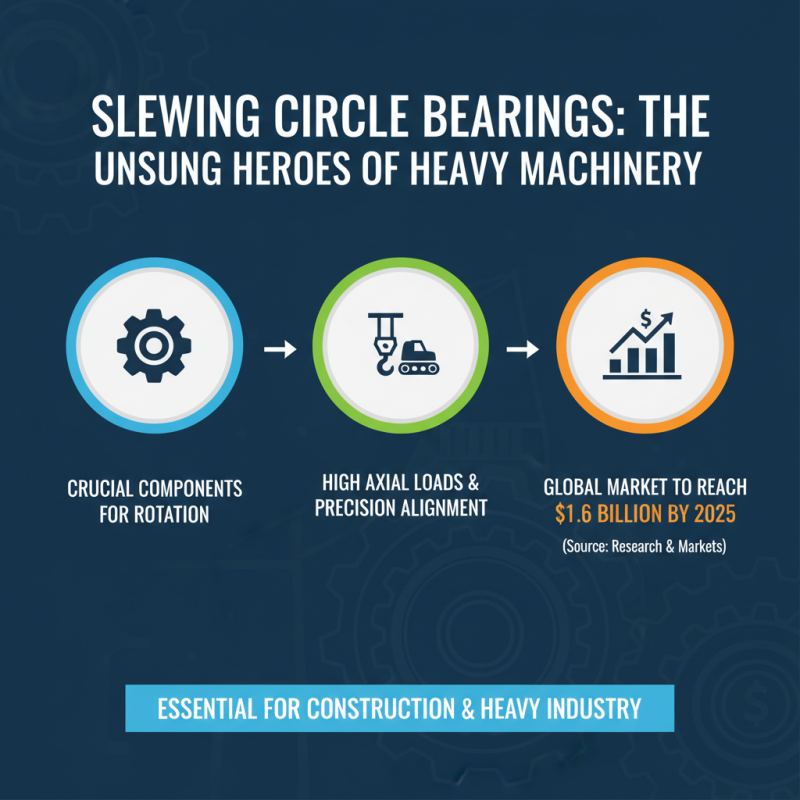
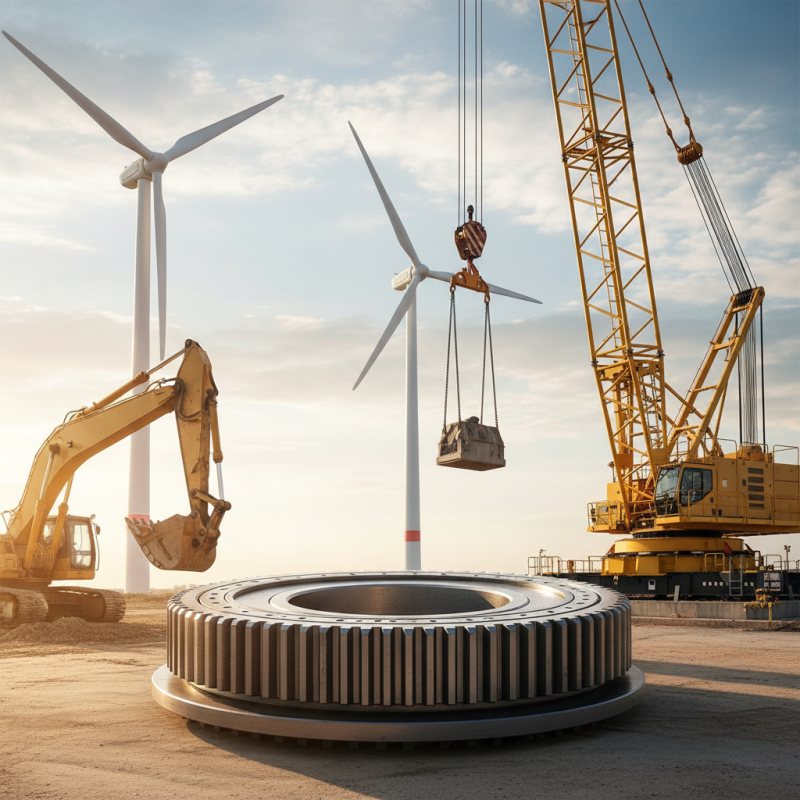
Slewing circle bearings are crucial components in various machinery, especially in construction and heavy industry, where they facilitate smooth rotational motion. These bearings are designed to accommodate high axial loads while maintaining structural stability and precise alignment. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global slewing bearing market is expected to reach $1.6 billion by 2025, indicating the increasing reliance on these components in heavy machinery applications.
One of the most common applications of slewing circle bearings is in cranes, where they enable the rotation of the crane's boom with minimal friction. This is essential for operations that require precise positioning, such as lifting and placing heavy loads. Additionally, slewing bearings are used in excavators and wheel loaders, allowing for effective pivoting and maneuverability on construction sites. The International Journal of Mechanics and Materials in Design highlights that improved bearing designs are leading to enhanced durability, which is critical in demanding environments.
Tips: When selecting slewing circle bearings for your machinery, consider factors such as load capacity, environmental conditions, and maintenance requirements. Regular inspections can significantly extend the life of these components, reducing downtime and improving overall efficiency. Furthermore, choosing the right lubricant can also enhance performance and longevity, ensuring your equipment operates smoothly under heavy loads.
Slewing circle bearings are essential components in various machinery applications, providing an efficient solution for rotational movement. One of the primary benefits of using these bearings in equipment design is their ability to support axial, radial, and moment loads simultaneously. This multi-directional load capacity enables engineers to create more compact and robust designs, optimizing space and enhancing the overall functionality of machines. As a result, slewing circle bearings are instrumental in improving the performance of equipment such as cranes, excavators, and industrial machines, where precise movement and structural integrity are paramount.
Another advantage of incorporating slewing circle bearings into design is the improved durability and reduced maintenance requirements. These bearings are engineered to withstand harsh working environments, which minimizes wear and tear over time. Their robust construction allows for smooth operation even under heavy load conditions, directly contributing to reduced downtime and maintenance costs. By facilitating longer operational life and enhanced reliability, slewing circle bearings offer significant value in the lifecycle of machinery, leading to more efficient manufacturing processes and increased productivity.
Maintenance and troubleshooting of slewing circle bearings are essential for ensuring the smooth operation of machinery. Regular inspection and lubrication of the bearings can significantly extend their lifespan and improve their performance. Operators should routinely check for signs of wear, such as cracks or excessive play, which can indicate that the bearing is approaching failure. Keeping the bearing surfaces clean and free from debris is also vital to prevent damage during operation.
In the event of operational issues, understanding the common problems associated with slewing circle bearings can facilitate timely troubleshooting. Regularly monitoring the temperature of the bearings is important, as overheating can signal inadequate lubrication or a misalignment. If noise or vibrations become evident during operation, it may suggest that the bearing is experiencing internal damage or that the mounting bolts are loose. Addressing these issues promptly can prevent more severe damage and costly repairs, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the machinery it supports.
| Application Area | Common Equipment | Load Capacity (kN) | Speed (rpm) | Maintenance Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Construction Machinery | Excavators, Cranes | 200 - 300 | 10 - 15 | Monthly |
| Renewable Energy | Wind Turbines | 150 - 250 | 5 - 10 | Quarterly |
| Marine Equipment | Jacking Units, Turntables | 100 - 200 | 8 - 12 | Monthly |
| Industrial Automation | Robotic Arms, CNC Machines | 50 - 150 | 15 - 20 | Bi-annual |